Your shopping cart is empty!
Categories
-
- - Amplifier Module
- - Arduino Compatible - Development Platform
- - Arduino Compatible Modules & Shields
- - Breakout Boards
- - Cables / Hookup wires
- - Displays
- - Enclosures
- - Magnets
- - Motors & Gears
- - Nuts & Bolts
- - Peltier Cooler Heater
- - PIR
- - Sensors
- - Servo's & Motors
- - Solar
- - Stand Alone Modules
- - Stepper Motor & Drivers
- - USB Programmers & Converters
- - Voltage Regulator & Chargers
- - RC Hobby Parts
-
- - AC DC Cooling Fans
- - Cable Ties
- - Day/Night Switches
- - Electrical Plugs & Connectors
- - Gate Remotes & Receivers (Universal)
- - Heat Shrink Sleeves
- - Insulation Tape
- - Lighting & Globes
- - Mains Power Cables
- - Power Supplies & AC/DC Adaptors
- - Security Lights LED Type
- - Solar Charge Controllers
- - Surge Protectors
- - Timers
-
- - Battery Holders
- - Breadboard
- - Bridge Rectifier
- - Buzzers
- - Capacitors
- - Crystals
- - Diodes
- - Electromechanical
- - Fuses
- - Headers
- - Heat Sinks
- - IC Sockets HQ
- - IC Sockets TIN
- - IC's --> Semiconductor
- - Inductors
- - Laser Units (CD Players)
- - Microcontrollers & CPU's
- - Opto Electronics
- - Panel Meters And Displays
- - Passive Components
- - Pilot Lamps & Fittings
- - Plugs & Sockets
- - Resistors
- - Rotary Potentiometer
- - Semiconductors
- - Sensors
- - Switches
- - Transformers
- - TVS Diodes
- - Veroboard / Stripboard
- - Voltage Regulators
- - Zener Diode
Zener Diode

A Zener diode is a diode which allows current to flow in the forward direction in the same manner as an ideal diode, but also permits it to flow in the reverse direction when the voltage is above a certain value known as the breakdown voltage, "Zener knee voltage", "Zener voltage", "avalanche point", or "peak inverse voltage".
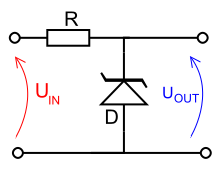
Zener diodes are widely used as voltage references and as shunt regulators to regulate the voltage across small circuits. When connected in parallel with a variable voltage source so that it is reverse biased, a Zener diode conducts when the voltage reaches the diode's reverse breakdown voltage. From that point on, the relatively low impedance of the diode keeps the voltage across the diode at that value
ZD 10v 0.5W Zener Diode DO35
..
R1.50
Ex Vat: R1.30
Ex Vat: R1.30
ZD 11v 0.5W Zener Diode
..
R1.50
Ex Vat: R1.30
Ex Vat: R1.30
ZD 12v 0.5W Zener Diode
..
R1.50
Ex Vat: R1.30
Ex Vat: R1.30
ZD 12v 1W 5% Zener Diode D041 1N4742A
..
R1.50
Ex Vat: R1.30
Ex Vat: R1.30
ZD 15v 0.5W 5% Zener Diode DO41
..
R1.50
Ex Vat: R1.30
Ex Vat: R1.30
ZD 15v 1W 5% Zener Diode D041 1N4744A
..
R1.50
Ex Vat: R1.30
Ex Vat: R1.30
ZD 15v 5W 1N5352B Zener Diode
..
R5.50
Ex Vat: R4.78
Ex Vat: R4.78
ZD 16v 0.5W Zener Diode
..
R1.50
Ex Vat: R1.30
Ex Vat: R1.30
ZD 18v 0.5W 5% Zener Diode DO35
..
R1.50
Ex Vat: R1.30
Ex Vat: R1.30
ZD 20v 0.5W 500mW Zener Diode
..
R1.50
Ex Vat: R1.30
Ex Vat: R1.30
ZD 22v 0.5W Zener Diode
..
R1.50
Ex Vat: R1.30
Ex Vat: R1.30
ZD 24v 0.5W Zener Diode
..
R1.50
Ex Vat: R1.30
Ex Vat: R1.30
ZD 27v 0.5W Zener Diode
..
R1.50
Ex Vat: R1.30
Ex Vat: R1.30
ZD 2v4 0.5W 5% Zener Diode D035
..
R1.50
Ex Vat: R1.30
Ex Vat: R1.30
ZD 30v 0.5W Zener Diode
..
R1.50
Ex Vat: R1.30
Ex Vat: R1.30
ZD 33v 0.5W Zener Diode
..
R1.50
Ex Vat: R1.30
Ex Vat: R1.30
ZD 36v 0.5W Zener Diode
..
R1.50
Ex Vat: R1.30
Ex Vat: R1.30
ZD 39v 0.5W Zener Diode
..
R1.50
Ex Vat: R1.30
Ex Vat: R1.30
ZD 3v3 0.5W 5% Zener Diode DO35
..
R1.50
Ex Vat: R1.30
Ex Vat: R1.30
Featured
Specials









-80x80.jpg)















